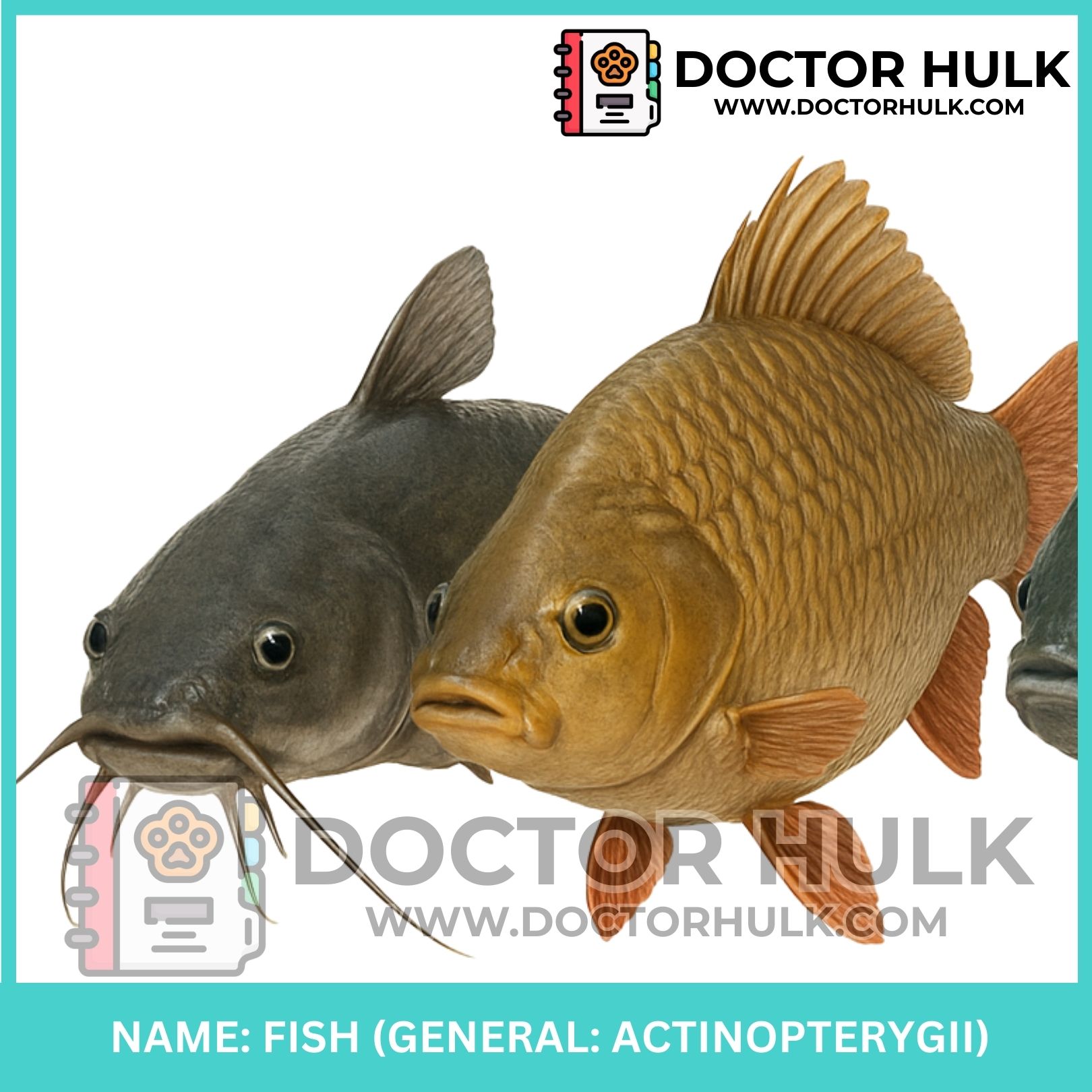
Fish are water-dwelling animals that breathe through gills and swim using fins. They are important to people for food, culture, and the environment. In Nigeria and many parts of Africa, catfish and tilapia are the two most common types eaten, raised, and sold.
Scientific Classification
-
Kingdom: Animalia
-
Phylum: Chordata
-
Class: Actinopterygii (ray-finned fishes)
-
Order & Family: Varies by type
Common Names
-
Catfish
-
Tilapia
-
“Point-and-kill” (catfish, in Nigerian restaurants)
-
“Water fowl” (local nickname for farmed fish)
Fish have many local names across tribes and are central to meals, business, and culture.
Geographic Distribution
Catfish and tilapia are found in:
-
Rivers, ponds, lakes, and streams
-
Man-made fish farms
-
Wet markets and restaurants across Africa
-
Warm climates across the globe
They are freshwater fish, although some tilapia can survive in slightly salty water
Image showing Freshly harvested catfishes on ice Source: Shutterstock)
Common species
1. Catfish (Clarias gariepinus)

Image showing a Large catfish with visible whiskers in shallow water (Source: Shutterstock)
Facts:
-
Popular in Nigerian fish farms
-
Grows fast and can survive in low oxygen
-
Very active and slippery
-
Main fish for “pepper soup” and barbecues
2. Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)

Image showing Tilapia swimming in a clear fish tank (Source: Shutterstock)
Key Facts:
-
Second most farmed fish in Africa
-
Easy to raise and hardy
-
White flesh with mild taste
-
Good for frying, boiling, and stews
What do they eat?
Catfish:
-
Insects, small fish, bloodworms
-
Floating pellets in farms
-
Organic waste in ponds
Tilapia:
-
Algae, aquatic plants
-
Farm feed pellets
-
Small insects and plankton
Both species are omnivores and adapt well to feed provided by fish farmers.
Fun facts
-
Catfish can survive outside water for hours if it’s moist.
-
Tilapia are sometimes called “aquatic chickens” because of their fast breeding.
-
Catfish use their whiskers to feel for food in the dark.
-
Tilapia can change sex depending on environmental needs.
-
A female tilapia can carry eggs in her mouth to protect them.
Importance to Humans
Positives:
-
Provide affordable protein for families
-
Offer jobs through fish farming and trading
-
Important in Nigerian cuisine (e.g., catfish pepper soup, grilled tilapia)
-
Easy to raise even in backyard ponds
Negatives:
-
Overcrowded ponds can lead to poor water quality
-
Escaped farmed fish may disturb natural ecosystems
-
Disease can spread quickly in shared ponds
Health & common issues
Fish need clean water and proper feeding to stay healthy.
Common Issues:
-
Fungal infections (white patches, cloudy eyes)
-
Gill disease from dirty water
-
Parasites (worms or lice in the skin or gills)
-
Poor growth due to overcrowding or poor feed
Tips for Healthy Fish:
-
Change pond water regularly
-
Avoid overfeeding
-
Quarantine sick fish
-
Use approved medications only when needed
Conservation & sustainability
Catfish and tilapia are not endangered, but wild fish populations are declining due to:
-
Overfishing in rivers and lakes
-
Pollution from chemicals and plastics
-
Habitat loss from human development
Fish farming is encouraged to reduce pressure on wild stocks, but it must be done responsibly.
Catfish vs Tilapia
| Feature | Catfish | Tilapia |
|---|---|---|
| Body Type | Long and slippery | Flat and scaly |
| Skin | No scales | Has scales |
| Taste | Rich and bold | Mild and sweet |
| Farm Needs | Oxygen control important | Breeds easily and grows fast |
| Popular Use | Pepper soup, grilled fish | Fried dishes, stews |

Image showing a farmer holding catfish and smiling (Source: SCIDev.net)
Do you have a fish farm, sick fish, or want to start aquaculture?, you can visit Doctor Hulk Veterinary Hospital Today or call 08143397614.

















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.