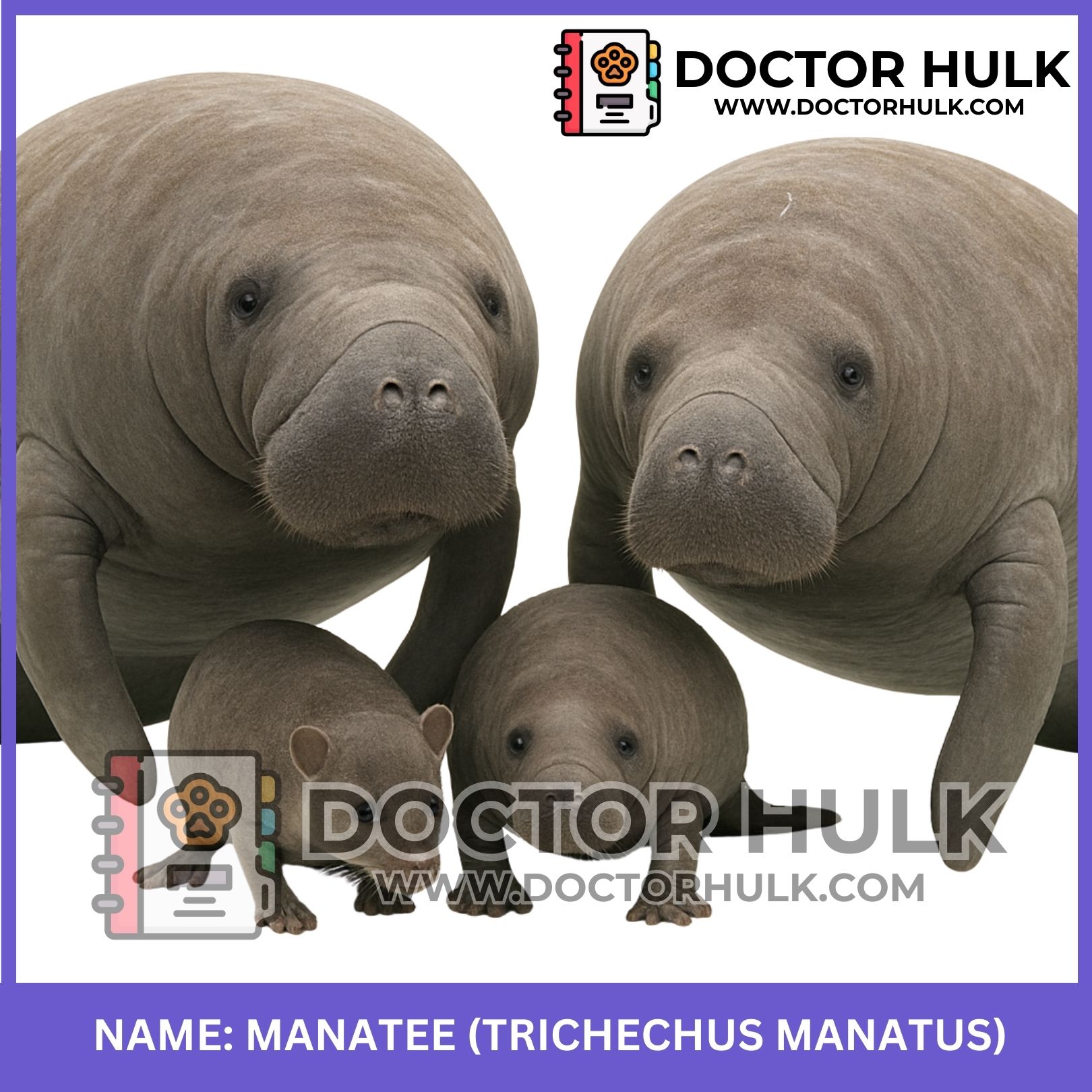
Manatees are large, peaceful water animals that slowly swim through rivers, lakes, and coastal seas. People often call them “sea cows” because they are calm and eat plants, just like cows on land.
Scientific Classification
-
Kingdom: Animalia
-
Phylum: Chordata
-
Class: Mammalia
-
Order: Sirenia
-
Family: Trichechidae
-
Genus: Trichechus
Common Names
-
Manatee
-
Sea Cow
-
West Indian Manatee
-
African Manatee
-
Amazonian Manatee
Geographic Distribution
Manatees live in warm, shallow waters. They are found in:
-
Florida and the Caribbean
-
West Africa
-
Amazon River Basin
They prefer slow-moving rivers, estuaries, lagoons, and coastal waters.
Image showing a manatee swimming near the surface of clear water (Source: Tampa Bay Times)
Physical Characteristics
-
Length: 2.5 to 4 meters (8 to 13 feet)
-
Weight: 400–600 kg (800–1,300 pounds)
-
Color: Gray or brown, with wrinkled skin
-
Tail: Wide, flat, and paddle-shaped
-
Body: Round and chubby, with small front flippers
-
Head: Large with a blunt snout and whiskers
Species of Manatees
1. West Indian Manatee (Trichechus manatus)
Found in the southeastern U.S., Gulf of Mexico, and Caribbean.
 Image showing a west Indian manatee near a boat (Source:iStock)
Image showing a west Indian manatee near a boat (Source:iStock)
-
Most commonly known type
-
Often seen near Florida
2. Amazonian Manatee (Trichechus inunguis)
Lives in the Amazon River and nearby streams.
Image showing amazonian manatees in freshwater river (Source: animals)
-
Smaller and darker
-
Only freshwater manatee
3. African Manatee (Trichechus senegalensis)
Found in West Africa’s rivers and coastal waters.
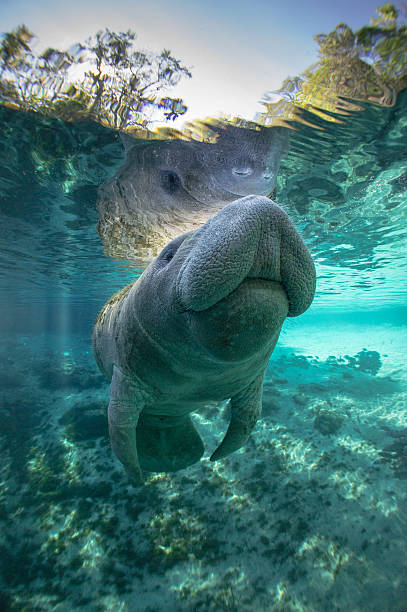 Image showing an african manatee swimming in a river (Source: iStock)
Image showing an african manatee swimming in a river (Source: iStock)
-
Least studied
-
Lives in both fresh and salt water
What do Manatees eat?
Manatees are herbivores. They eat only plants, such as:
-
Seagrass
-
Water hyacinths
-
Algae
-
River weeds
They can eat over 45 kg (100 pounds) of plants each day.
Fun facts about Manatees
-
Manatees breathe air, but can hold their breath for 15–20 minutes.
-
They have no natural enemies, their biggest threat is humans.
-
Their teeth are always replaced as they wear out, like a conveyor belt.
-
Despite their size, manatees are gentle and quiet.
-
Manatees can live up to 60 years in the wild.
Importance to Humans
Positive Roles:
-
Help control aquatic plant growth
-
Attract tourists and promote conservation
-
Used in traditional stories and beliefs
Challenges:
-
Sometimes injured by boat propellers
-
Can suffer from pollution or habitat loss
-
Sensitive to cold temperatures
Health & common issues
Manatees are tough but still need care and protection, especially in areas with human activity.
Common health problems include the following:
-
Boat injuries (cuts or broken bones)
-
Cold stress syndrome
-
Parasites and digestive issues
-
Starvation when seagrass dies off
Veterinary Tips (for sanctuaries or wildlife workers):
-
Monitor for wounds and breathing issues
-
Keep injured manatees warm
-
Feed high-fiber aquatic plants
-
Watch for algae blooms or pollution in water
Conservation Status
Most manatees are vulnerable or threatened. Their main threats are:
-
Boat collisions
-
Loss of seagrass beds
-
Pollution
-
Cold weather events
Many countries now protect manatees by law, with rescue centers and awareness programs in place.
Manatee vs Dugong: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Manatee | Dugong |
|---|---|---|
| Tail | Flat and rounded | Shaped like a dolphin’s |
| Habitat | Rivers and coasts | Always in salt water |
| Size | Bigger | Slightly smaller |
| Range | Americas, Africa | Indian & Pacific Oceans |
 Image showing a manatee swimming with a baby (Source: Shutterstock)
Image showing a manatee swimming with a baby (Source: Shutterstock)
If you want to learn more about marine animals or you need help with animal education, check through our website or reach out to us at Doctor Hulk Veterinary Hospital. You can also simply call 08143397614.
















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.