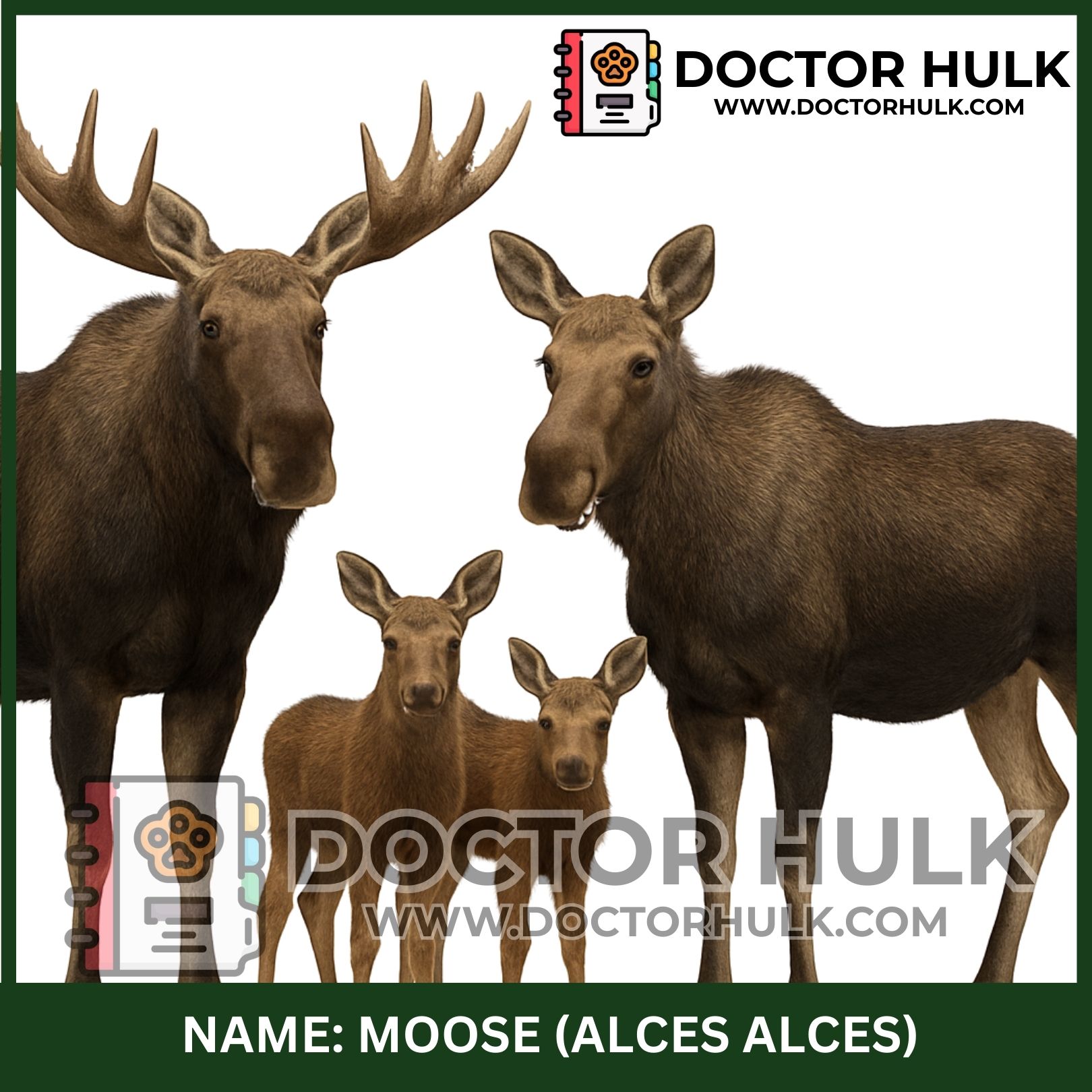
The moose is the largest member of the deer family. It’s known for its long legs, big antlers, and peaceful nature. Moose live in cold forests and are mostly found in the northern parts of the world. They are shy but strong animals that love quiet and water.
Scientific Classification
-
Kingdom: Animalia
-
Phylum: Chordata
-
Class: Mammalia
-
Order: Artiodactyla
-
Family: Cervidae
-
Genus: Alces
-
Species: Alces alces
Common Names
-
Moose (North America)
-
Elk (Europe and Asia, not to be confused with North American elk)
Geographic Distribution
Moose are found in:
-
North America – Canada, Alaska, northern U.S. states
-
Europe – Norway, Sweden, Finland
-
Asia – Russia and Siberian forests
They live in cold climates, near lakes, rivers, and wetlands.

Image showing an adult moose drinking from a forest lake (Source: Freepik)
Physical Characteristics
-
Height: Up to 2.1 meters (7 feet) at the shoulder
-
Weight: 400–700 kg (880–1,500 lbs)
-
Color: Brown to black fur
-
Antlers: Males grow wide, flat antlers yearly
-
Snout: Long nose with a flap of skin called a “bell” under the throat
-
Legs: Long and powerful, good for deep snow and swimming
Species of Moose (Subspecies)
Here are a few common moose subspecies:
1. Alaskan Moose
 Image showing a massive moose with wide antlers in snowy terrain (Source: Pinterest)
Image showing a massive moose with wide antlers in snowy terrain (Source: Pinterest)
-
Largest type
-
Found in Alaska and parts of Canada
-
Males have antlers over 6 feet wide
2. Eastern Moose
 Image showing a moose walking through forest path(Source: Anchorage Bike Tours)
Image showing a moose walking through forest path(Source: Anchorage Bike Tours)
-
Found in eastern Canada and northeastern U.S.
-
Slightly smaller than the Alaskan moose
3. Eurasian Elk (European Moose)
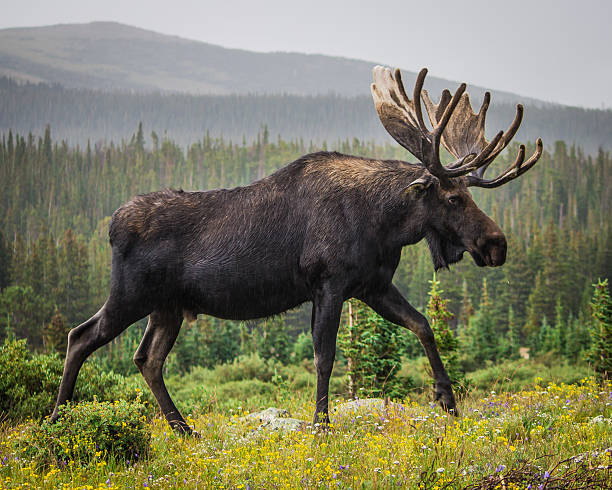 Image showing an European moose standing in grass (Source: iStock)
Image showing an European moose standing in grass (Source: iStock)
-
Found in Russia and northern Europe
-
More slender, with different antler shapes
Fun facts about Moose
-
A moose can run up to 35 mph (56 km/h).
-
Moose are excellent swimmers and can dive 6 meters deep!
-
Their antlers fall off each winter and grow back in spring.
-
Moose have poor eyesight but a strong sense of smell.
-
Despite their size, they are very quiet in the forest.
Importance to Humans
Positive Impact:
-
Provide food and fur in traditional cultures
-
Attract tourists and photographers
-
Play an important role in forest balance by eating certain plants
Challenges:
-
Moose sometimes cause car accidents in forested roads
-
In some areas, they damage young trees on farmlands
Health & common issues
Moose in the wild face several dangers:
Common health problems include the following:
-
Parasites like ticks and brainworm
-
Injuries from fights (especially during mating season)
-
Malnutrition in harsh winters
-
Traffic accidents
Many countries have hunting limits and protection laws in place.
What do Moose eat?
Moose are herbivores. They eat:
-
Leaves, twigs, and bark
-
Water plants (they often wade into lakes to feed)
-
Shrubs and tree shoots in winter
They eat a lot to support their huge bodies.
Veterinary tips (for zoos or sanctuaries):
-
Moose need open space and cold weather
-
Their diet must include fresh greens and water plants
-
Check regularly for parasites and skin issues
Conservation Status
-
Moose are not endangered overall, but some subspecies have declining populations.
-
Threats include:
-
Climate change
-
Habitat loss
-
Disease
-
Overhunting (in some areas)
-
Moose vs Deer: What’s the difference?
| Feature | Moose | Deer |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Much larger | Smaller and lighter |
| Antlers | Broad and flat (males) | Branched and pointed |
| Habitat | Cold, northern forests | Found worldwide |
| Behavior | More solitary | Often live in groups |
Just in case you need questions about large wildlife or you need animal education materials, you can reach out to use at Doctor Hulk Veterinary Hospital, or call 08143397614.

















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.