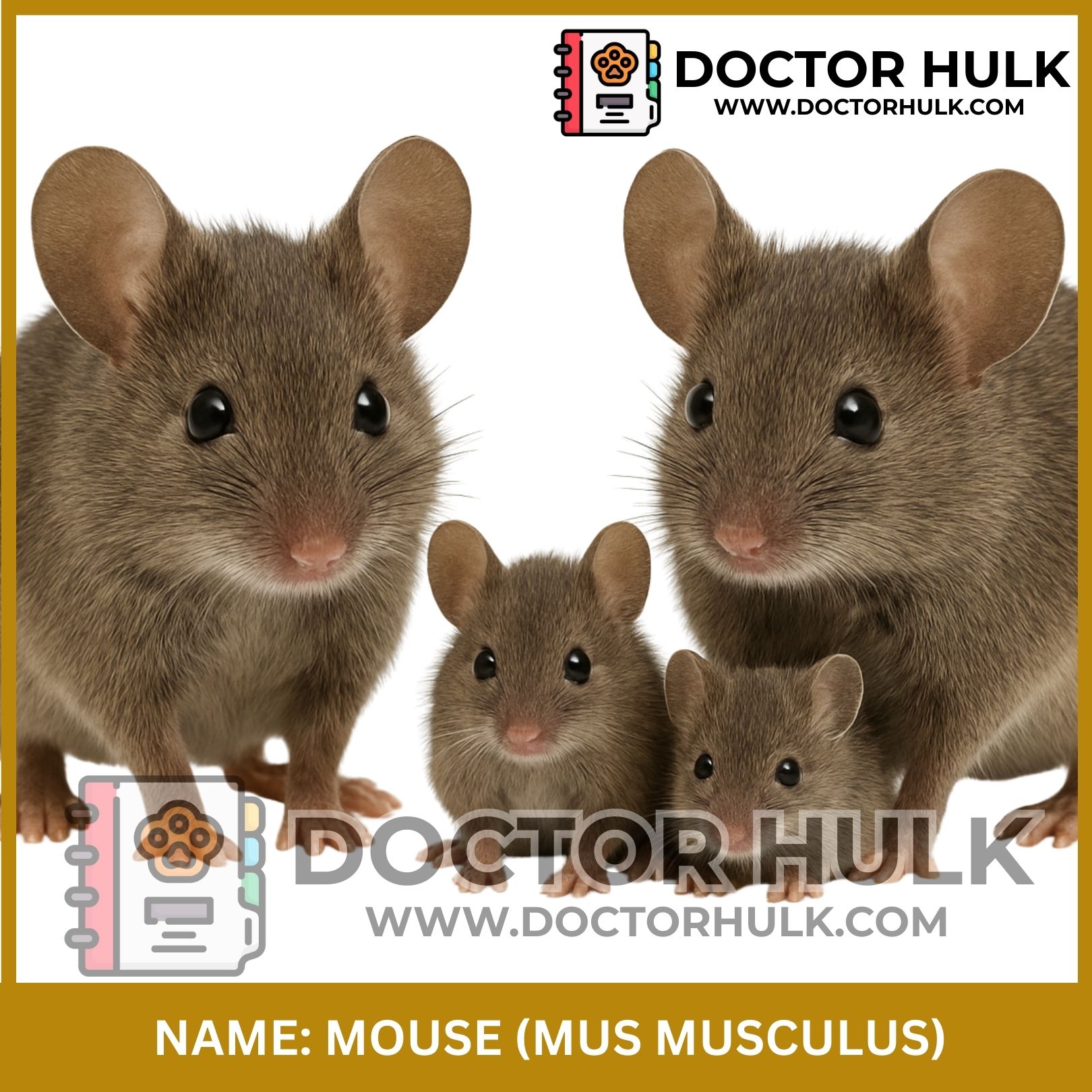
Mice are small animals known for their sharp front teeth, fast movements, and squeaky sounds. Though tiny, they are part of nature, science, and even human homes, sometimes good, sometimes not.
Scientific Classification
-
Kingdom: Animalia
-
Phylum: Chordata
-
Class: Mammalia
-
Order: Rodentia
-
Family: Muridae
-
Genus: Mus
-
Common Species: Mus musculus (House Mouse)
Common Names
-
Mouse
-
House Mouse
-
Field Mouse
-
Pet Mouse
-
Fancy Mouse (bred for pets)
Geographic Distribution
Mice are found all over the world. They live in:
-
Fields and farmlands
-
Forests
-
Cities and houses
-
Laboratories and pet shops
Image showing a mouse nibbling on a cheese (Source: Business insider)
Physical Characteristics
-
Size: 6 to 10 cm (2.5 to 4 inches) long
-
Tail: Long and often hairless
-
Color: Usually grey or brown, but pet mice can be white or spotted
-
Ears: Round and large for their size
-
Teeth: Sharp front teeth that never stop growing
Species of Mice
1. House Mouse (Mus musculus)
The most common type. Lives in homes, farms, and buildings.
 Image showing house mice near food crumbs (Source: Shutterstock)
Image showing house mice near food crumbs (Source: Shutterstock)
-
Small and fast
-
Good climber and jumper
-
Often lives near humans
2. Field Mouse (Various species)
Wild mouse often found in fields and forests.
 Image showing a field mouse hiding in leaves (Source: iStock)
Image showing a field mouse hiding in leaves (Source: iStock)
-
Shy and quick
-
Feeds on seeds and plants
-
Hides in burrows
3. Fancy Mouse
A house mouse bred to be a pet.
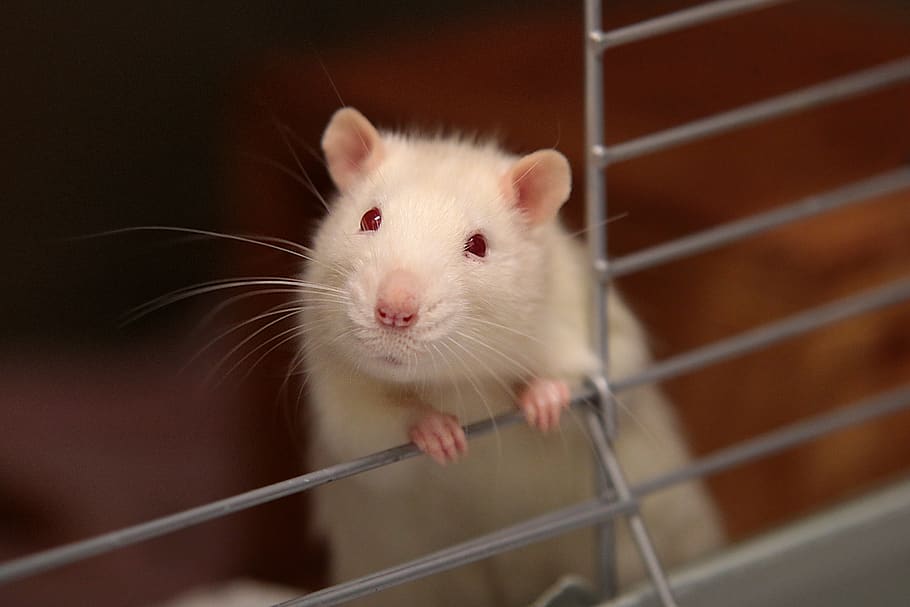 Image showing white fancy mouse in a cage (Source: Walpaper Flare)
Image showing white fancy mouse in a cage (Source: Walpaper Flare)
-
Comes in many colors
-
Friendly and playful
-
Can be trained and held
What do Mice eat?
Mice are omnivores, but mostly eat plant-based food.
Their diet includes:
-
Grains and seeds
-
Fruits and vegetables
-
Insects (occasionally)
-
Food scraps (when living near people)
Fun facts about Mice
-
Mice can squeeze through holes the size of a pen!
-
A mouse’s front teeth never stop growing.
-
Mice can have babies every 3 weeks!
-
They are used in labs for medical research.
-
Mice communicate using high-pitched squeaks.
Importance to Humans
Positive Roles:
-
Help in medical and genetic research
-
Kept as pets (especially fancy mice)
-
Help control insects in some ecosystems
Challenges:
-
Can damage food and property
-
Spread diseases if not controlled
-
Multiply very fast if not managed
Health & common issues
Mice, like all animals, can suffer from diseases and injuries, especially in captivity or poor environments.
Common Health Problems:
-
Respiratory infections (especially in dirty cages)
-
Parasites like mites and fleas
-
Tumors or lumps in older mice
-
Injuries from falls or fights
Veterinary Tips:
-
Keep cages clean and dry
-
Feed balanced food
-
Handle gently to reduce stress
-
Regular check-ups for pet mice
Conservation Status
Most mice are not endangered, in fact, they are one of the most widespread mammals on Earth.
However, some rare wild mice (like the wood mouse or spiny mouse) may face threats due to:
-
Habitat loss
-
Pesticides
-
Predators
Mouse vs Rat: What’s the difference?
| Feature | Mouse | Rat |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Small (6–10 cm) | Larger (20+ cm) |
| Ears | Larger for their body | Smaller proportionally |
| Tail | Long and thin | Thicker and scaly |
| Behavior | Shy, quick | Bolder, smarter |
 Image showing a pet fancy mouse nibbling on a treat (Source: StockCake)
Image showing a pet fancy mouse nibbling on a treat (Source: StockCake)
If you need help with rodents or small pet care, do not hesitate to reach out to us at Doctor Hulk Veterinary Hospital, or call 08143397614.
















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.